Mars Noire Naked - Exploring The Red Planet's Secrets
There is something truly captivating about the bright, reddish point of light that often graces our night sky. It is, you know, a place that has long held a special spot in our collective imagination, appearing as a distant, yet somehow familiar, neighbor. For generations, people have looked up and wondered about this particular world, a celestial body that, in a way, seems to call out to us from across the vastness of space. We are, it seems, always eager to learn more about what lies beyond our own home, especially when it comes to places that might just hold answers to big questions about life itself. This piece aims to pull back the curtain, giving you a raw, unfiltered look at this amazing planet.
This reddish world, the one that sits four spots out from the sun, is actually one of the easiest planets to pick out when you gaze up at the stars. It stands out, quite clearly, with its distinct color, almost like a beacon in the darkness. You can, for instance, often spot it without needing any special equipment, just your own eyes. It has, too, been a source of fascination for many, many years, prompting us to send machines to its surface to gather information and send it back home. So, in some respects, it's a place we feel we know, even though it's so far away.
Over time, our understanding of this intriguing planet has grown quite a bit, thanks to the tireless efforts of various space missions. We have, you see, sent many different types of robots to its surface, each one designed to explore its unfamiliar ground and send back precious details. These efforts have, apparently, brought us a wealth of information, revealing aspects of this distant world that were once purely the stuff of dreams. It is, really, a testament to human curiosity and our desire to uncover the truth about the universe around us. We are, after all, always looking for what else might be out there.
Table of Contents
- What Makes Mars So Alluring?
- Is Mars Really a "Naked" World of Deserts?
- How Do We Know So Much About Mars's Past?
- What Has the "Mars Noire" Revealed About Life?
- What Are Mars's Physical Traits?
- Why Does Mars Have That "Naked Red" Look?
- Does Mars Share Anything with Our Home Planet?
- Exploring Mars - A "Noire Naked" View?
What Makes Mars So Alluring?
There is, quite simply, something about Mars that draws us in. It is, for one thing, the fourth planet from the sun, placing it in a spot that feels both close and far away at the same time. This planet, a bit like a smaller sibling to our own Earth, is one of our home planet's two closest celestial neighbors, with Venus being the other. Its presence in the night sky is, typically, quite noticeable, especially when it's particularly bright. This easy visibility, you know, makes it a frequent topic of conversation and a common target for backyard stargazers. It truly stands out, a reddish point against the dark.
Its distinctive color is, perhaps, one of the first things that catches your eye. This planet, you see, has a very clear reddish look, almost like old, rusty metal. It's a color that has earned it the nickname "the Red Planet," and it's a name that, frankly, sticks. This appearance makes it, in a way, unique among the planets we can readily observe without a telescope. The sight of it, bright and red, against the backdrop of countless stars, is pretty striking. It truly is, quite literally, a shining example of the beauty found in our solar system, offering a visual treat for anyone who looks up.
Is Mars Really a "Naked" World of Deserts?
When we talk about Mars, we often picture a vast, empty expanse, a very cold, dry stretch of land. It is, in fact, often described as a desert world within our solar system, a place where water, as we know it, seems scarce on the surface. This perception of a bare, unadorned landscape is, in some respects, accurate. The surface of Mars is, after all, exposed to the harshness of space, with a thin atmosphere and no large bodies of liquid water flowing openly today. So, in a way, it presents a very raw, uncovered appearance, like a world laid bare for all to see.
However, the idea of Mars being entirely a "naked" desert might be a little too simple. Evidence has, you know, been found that suggests this planet once had water moving across its surface. This means that, at some point in its long history, it might have been a place with rivers or lakes, perhaps even small seas. The presence of such features would, clearly, paint a very different picture than the dry, dusty world we see today. So, while it appears as a chilly, dry place now, its past tells a story of something more dynamic, something with more fluidity, offering a glimpse into what a "mars noire naked" might have looked like millions of years ago.
How Do We Know So Much About Mars's Past?
Our current understanding of Mars, including hints about its earlier days, comes from a great deal of careful investigation. Mars is, as a matter of fact, one of the most thoroughly examined bodies in our solar system. We have, you know, sent many different types of robots, called rovers, to travel across its unfamiliar ground. These machines are, basically, like mobile scientific laboratories, equipped with tools to study the planet's rocks, soil, and atmosphere. Their presence on the surface allows us to gather direct information, something that would be impossible from Earth.
These robotic explorers have, over the years, collected many signs and clues about Mars's history. They have, for instance, drilled into the ground, scooped up samples, and taken countless pictures. The information they send back helps scientists piece together the story of this distant world. It's a bit like putting together a giant puzzle, where each piece of data, each image, helps us see the bigger picture. So, we are, in a way, getting a very close-up look at its past, thanks to these amazing machines that work tirelessly on its surface, revealing its secrets.
What Has the "Mars Noire" Revealed About Life?
One of the most exciting parts of exploring Mars is the search for signs of life, either in its past or present. Recently, one of our robotic explorers, a rover, took a sample from a new area, a spot with features that could tell us if the ground beneath Mars's surface once had conditions good enough for living things. This kind of exploration is, you see, incredibly important because it looks at places where life might have been protected from the harsh surface conditions. It's a way of looking for the subtle hints, the "mars noire" aspects, that might be hidden away.
The idea is that if water was present underground, and if there were sources of energy, then simple life forms might have had a chance to exist. The data and images that are being collected from these underground samples are, therefore, very important for our understanding. They could, potentially, show us whether Mars, in its earlier times, was a place where tiny living things could have made a home. So, this search for signs of life, even very small ones, is a central part of why we continue to explore this fascinating planet, looking for any sign of its hidden potential.
What Are Mars's Physical Traits?
Beyond its reddish color and its potential for past water, Mars has some very specific physical characteristics that set it apart. It is, for example, the seventh largest planet in our solar system when we consider its overall size. With a measurement of about 2,106 miles from its center to its edge, Mars is, quite literally, about half the distance across compared to Earth. This makes it a considerably smaller world than our own, but still a substantial one in the grand scheme of things. Its dimensions are, basically, a key part of what makes it unique among its planetary neighbors.
When it comes to how much it pulls things down, Mars has a surface gravity that is about 37.5 percent of Earth's. This means that if you were to stand on Mars, you would feel much lighter than you do here. A jump that might take you a few inches on Earth would, you know, send you much higher on Mars. Its overall distance across is about 4,228 miles, or 6,804 kilometers, which further illustrates its size relative to other planets. So, in many ways, it's a world that feels both familiar in some aspects, yet quite different in its fundamental physical makeup.
Why Does Mars Have That "Naked Red" Look?
The reason Mars is sometimes called the Red Planet is, you know, quite straightforward. It gets its distinctive color because of the reddish stuff in its dirt. This reddish material is, basically, iron that has rusted, very much like the rust you might see on an old piece of metal here on Earth. When iron is exposed to oxygen, it undergoes a process that gives it that familiar reddish-brown hue. On Mars, this rusty iron is, quite literally, everywhere on its surface, covering vast areas and giving the entire planet its striking appearance.
This rusty dust is, in a way, what gives Mars its "naked red" look, a color that is so prominent it can be seen from millions of miles away. The particles of this reddish dust are very fine, and they are often picked up by the winds on Mars, creating dust storms that can, at times, cover large portions of the planet. These storms, you see, further contribute to the overall reddish atmosphere, making the entire world appear even more intensely red. So, it's not just the ground, but also the air, that carries this signature color, making it truly a red world.
Does Mars Share Anything with Our Home Planet?
Even though Mars is a different world, it actually shares some surprising similarities with Earth. Just like our home planet, Mars experiences different times of the year, known as seasons. These seasonal changes are, basically, due to the tilt of its axis, much like how Earth's tilt causes our own seasons. So, in some respects, it goes through its own version of summer, autumn, winter, and spring, albeit with very different temperatures and conditions than what we're used to here.
Mars also has, you know, areas of ice at its top and bottom, similar to Earth's polar ice caps. These frozen regions are, in fact, made up of both water ice and frozen carbon dioxide, often called dry ice. Furthermore, this planet has features that remind us of Earth's own geology. It has, for instance, very large mountains that are actually volcanoes, some of which are truly enormous. There are also deep cuts in its surface, known as canyons, which stretch for vast distances. And, perhaps most surprisingly, Mars even has its own kind of weather, with winds and dust storms moving across its surface. It's quite remarkable, really, how many parallels we can find.
Exploring Mars - A "Noire Naked" View?
The quest to explore Mars continues, offering us an ever more complete picture of this intriguing world. Every mission, every piece of information sent back, helps us get a more unfiltered, "noire naked" view of what Mars truly is. We are, you know, constantly learning new things about its past, its present, and what its future might hold. The robots we send there are like our eyes and hands, reaching out across space to touch and feel this distant planet. They are, in a way, our proxies in this grand adventure of discovery, allowing us to experience Mars without actually being there ourselves.
This ongoing exploration is, quite literally, peeling back the layers of mystery that have surrounded Mars for so long. From its two rather odd little companions, its moons, to the potential for life beneath its surface, Mars continues to surprise us. It is, basically, a cold, desert world, but one that holds many secrets within its rusty red appearance. The images and details being collected are, for example, helping us to piece together a comprehensive story of this planet, moving us closer to a full understanding of its unique characteristics. So, the journey of discovery is far from over, and each new piece of information brings us closer to truly seeing Mars for what it is.
This article has explored Mars, the fourth planet from the sun, highlighting its status as one of the most explored bodies in our solar system, with rovers gathering extensive evidence. We've looked at its position as the seventh in size and mass, its conspicuous reddish appearance, and its proximity to Earth. The piece touched upon recent rover discoveries, including samples from new regions that could indicate past environments suitable for life. We also discussed Mars's distinct rusty red look, its two unusual moons, and its nature as a cold, desert world. Physical attributes such as its radius, diameter, and surface gravity were covered. Finally, the article noted Mars's similarities to Earth, including seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons, and weather, all contributing to a clearer picture of this fascinating "Red Planet."
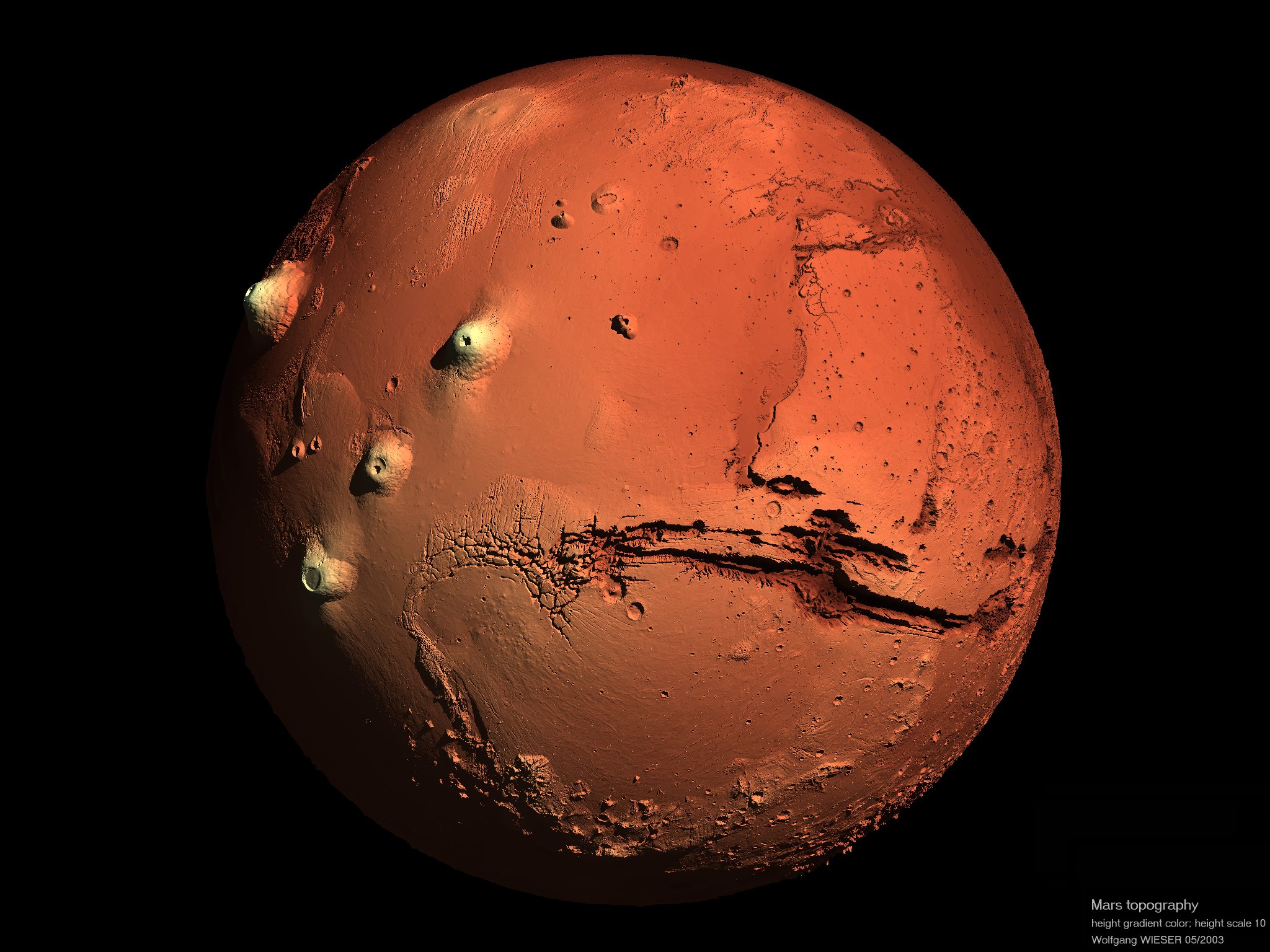
First rendered images of Mars
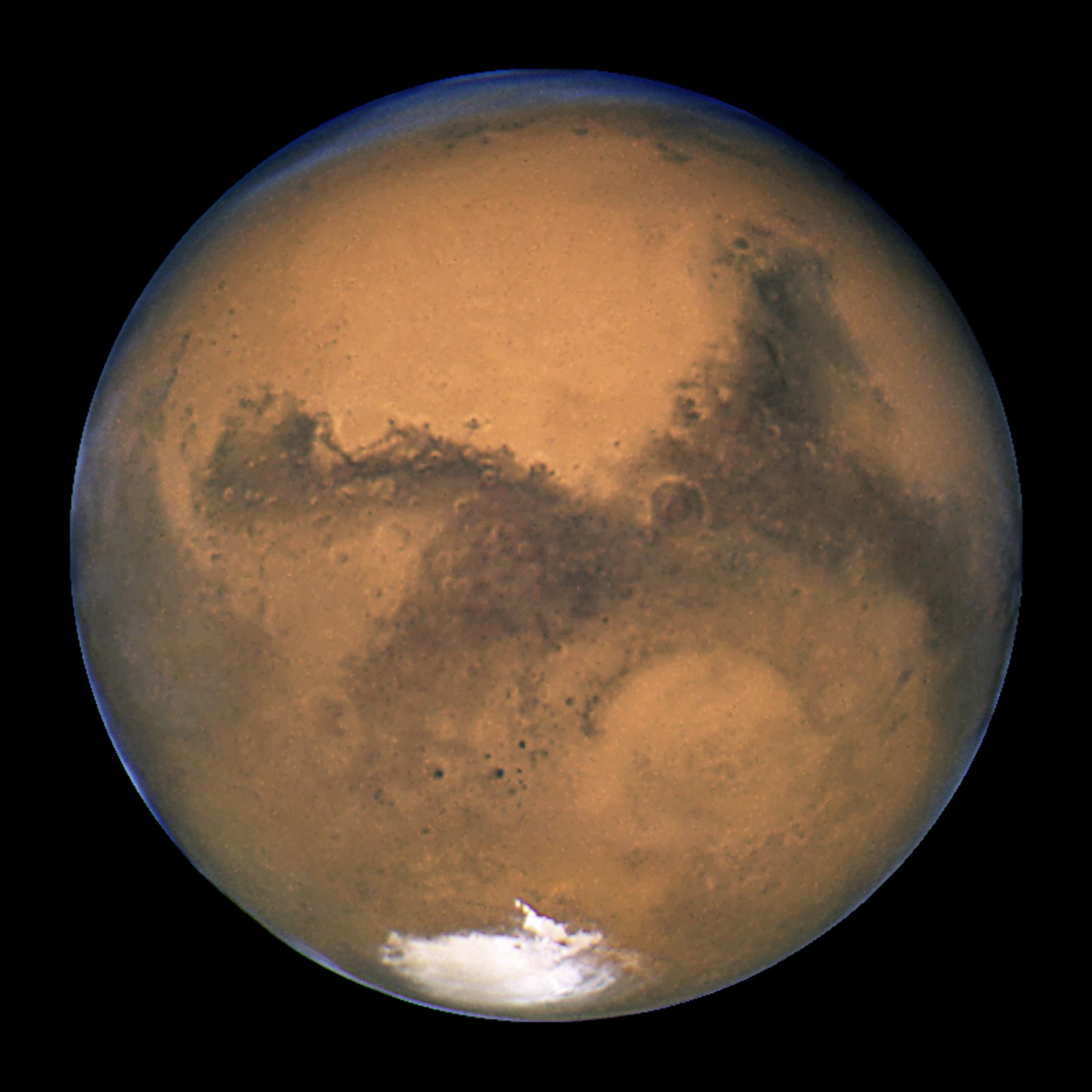

Overview | Mars – NASA Solar System Exploration

Planet Mars Wallpapers - Wallpaper Cave